24-12-2024
ADA MED SUPPLY LIMITED
Article tag: Neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulator Cardiopulmonary resuscitation model BIX-CPR160
In emergency medical education, especially for newborn nursing, simulation training has become an indispensable link. Neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulator, as a high-fidelity teaching tool, has greatly improved the emergency response ability and clinical skills of medical students. This is important not only for the development of skills, but also for the ability to provide real-world simulations, enhance emergency response capabilities, and reduce clinical errors.
Provide realistic training scenarios
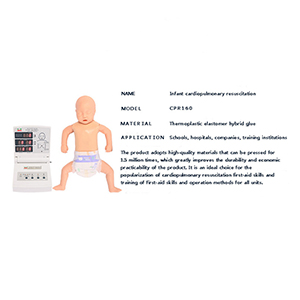
Neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulator
Neonatal CPR simulators can simulate emergency situations such as cardiac arrest and apnea in newborns to help students practice in a risk-free environment. This simulation not only familiarizes students with the resuscitation steps, but also allows them to feel and adapt to stressful situations in the clinic. Studies have shown that students can master resuscitation skills better in simulation training than in traditional teaching. One survey showed that students who underwent neonatal resuscitation simulation training had a success rate of about 40% higher than those who only received theoretical training.
Strengthen emergency decision-making capacity
Neonatal CPR simulators can simulate different clinical situations and pathological states, which not only helps students master operational skills, but also exercises their decision-making ability in emergency situations. For example, simulators can provide a variety of feedback through airway management, chest compressions, drug use, and other actions. This dynamic feedback helps students identify and resolve problems that may arise during the recovery process. The data showed that after the simulation training, the reaction time of medical students in handling complex resuscitation situations was reduced by nearly 20%.
Reduce clinical errors
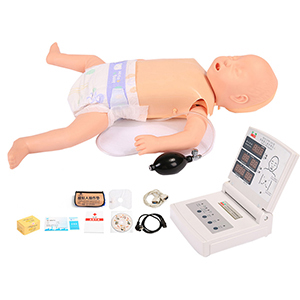
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation model
In emergency medicine, time is of the essence, and any delay or operational error can have a serious impact on the patient. Through simulation training, students are able to practice repeatedly without endangering their lives, reducing errors in actual operation. For example, simulation training allows students to familiarize themselves with the specific steps of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, thus reducing medical errors caused by inproficiency.
Data support
The study also showed that students who used simulation training experienced significant improvements in their technical mastery and confidence when assessing and handling neonatal CPR. One study in the US showed that medical students who received simulated training scored about 30 per cent higher in practical assessments than those taught in traditional classrooms. In addition, simulation training can effectively improve the operational consistency of newborn resuscitation, so that students can make a more accurate and consistent response in the face of emergency situations.
conclusion
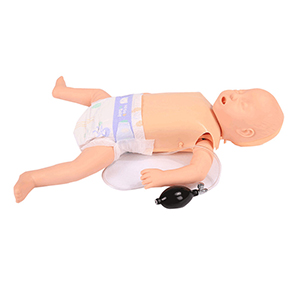
Neonatal CPR simulators not only enhance students' skill training, but also significantly improve their emergency response and clinical judgment by providing dynamic feedback and emergency scenarios. By combining theoretical and simulation training, medical education can provide students with more comprehensive and practical training, ultimately improving the quality and safety of neonatal care. Therefore, neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulators are undoubtedly a key component of emergency medical education.