28-12-2024
ADA MED SUPPLY LIMITED
Thoracic puncture drainage is an important treatment method for treating pleural effusion, pneumothorax and other diseases, which is often used in emergency and intensive care. Although this technology seems simple, the actual operation involves many considerations such as accurate judgment, appropriate selection of puncture sites, and drainage management. Because of the serious complications that can result from misoperation, the doctor's clinical decision-making ability is particularly critical. So, can thoracic puncture and drainage training, especially the use of training models, improve the clinical decision-making ability of physicians? Let's look at this in terms of personal growth, clinical significance, industry expert opinion, and data support.
1. Personal growth: Improve skills and decision-making confidence
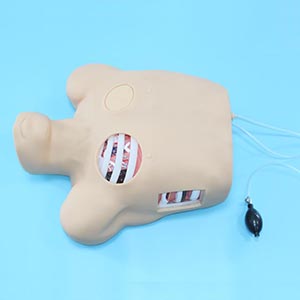
Thoracic Puncture Drainage Training
For doctors, especially beginners or inexperienced young doctors, thoracic puncture drainage is a challenging skill. Successful operation is not only a matter of surgical skills, but also the doctor's comprehensive judgment of multiple factors such as the patient's situation, puncture site, and equipment selection. The simulation training model provides a risk-free, repeatable platform that allows physicians to gain experience in a simulated environment, improve confidence, and make faster and more accurate decisions when confronted with real cases.
The data back it up: One survey found that doctors who trained with a thoracopuncture drainage model improved the accuracy of clinical decisions by 20% within three months of their practice. Simulation training enables them to quickly determine the best course of action when facing different clinical situations, reducing the error rate.
2. Clinical significance: improve the accuracy and safety of the operation
The clinical significance of thoracic puncture drainage is to remove the effusion or gas in the thoracic cavity timely and accurately, relieve the symptoms of patients, and improve the respiratory function. However, this procedure is risky, and the wrong puncture Angle, improper site selection, or inadequate drainage may lead to serious consequences such as pneumothorax, infection, or bleeding. The simulation training model can help doctors to get familiar with various possible complex situations through repeated operation and simulation of different clinical scenarios, so as to make more accurate decisions in actual operation and reduce unnecessary complications and risks.
Expert opinion: Well-known thoracic surgery experts said that as a highly simulated teaching tool, the thoracic puncture drainage model can allow doctors to "anticipate" and deal with possible complex situations in advance, such as irregular fluid positions and internal thoracic lesions. Through these trainings, doctors' clinical decision-making ability has been significantly improved.
3. Industry experts: The positive impact of model training on doctors' clinical decision-making
Medical education experts generally believe that traditional teaching methods and classroom explanations often fail to fully simulate real clinical decision-making situations. By providing highly simulated operation experience, the training model of thoracic puncture drainage can effectively improve doctors' surgical skills and clinical judgment. Experts emphasize that thoracic puncture and drainage training is not only about learning how to perform the procedure, but more importantly, learning how to evaluate the specific conditions of different patients to make the best treatment decisions.
Expert advice: With the continuous progress of medical technology, doctors' clinical decisions are no longer solely dependent on experience, but more rely on accurate data support and comprehensive technical capabilities. Training with simulation models helps physicians quickly identify and respond to complex situations in practice, especially in emergency or critical care Settings, and make timely and accurate decisions.
4. Data support: simulation training effect
The research data show that the training model of thoracic puncture and drainage has a significant effect on improving doctors' clinical decision-making ability. According to the results of a study of different levels of doctors, doctors who participated in simulation training were better than those who did not undergo simulation training in terms of operational accuracy, clinical judgment speed, and complication rate.
Data support: In a study involving 100 emergency department physicians, test results after training a model using thoracic puncture drainage showed a 15% improvement in procedure success and a 10% reduction in complications. More importantly, the response time to clinical decisions was reduced by 25%, especially in the treatment of acute pneumothorax or large pleural effusion, and the decision-making ability and operational accuracy of physicians were significantly enhanced.
5. Conclusion: Improve doctors' clinical decision-making ability to ensure patient safety
To sum up, the thoracic puncture and drainage training model undoubtedly plays a positive role in improving doctors' clinical decision-making ability. Through simulation training, doctors can not only improve the accuracy of their operations, but also make more informed decisions in complex and urgent clinical situations. This simulation training can help doctors deal with the operation of thoracic puncture drainage more confidently in the clinic, reduce complications, improve patient safety and treatment effect. With the development of medical training technology, training model will become a key tool to improve doctors' skills and decision-making ability, and lay a solid foundation for the improvement of clinical care quality.